Core 510i
The Q-SYS Core 510i represents the second generation of QSC’s Integrated Core Platform. It features eight I/O card slots, which can be populated with any combination of Q-SYS I/O cards allowing for up to 128x128 local channels plus a total of 256x256 network channels for diverse connectivity options.
Note: This topic provides an overview of the Core 510i. For installation instructions and other documentation, see the Core 510i product page online.
|
Local I/O Channels |
Up to 32 analog, up to 128x128 AES/CobraNet/Dante/AVB |
|
Network Audio Channels |
256 x 256 |
|
AEC Processors |
64 |
|
Multitrack Audio Players |
16 (upgradable to 128) |
|
Local I/O Card Capacity |
8 |
|
VoIP Instances |
64 |
|
Q-SYS peripheral limit |
It is recommended not to exceed 128 NL, NM, or QIO Series peripherals in a design in any combination. |
- Q-SYS Core processing in a flexible chassis featuring 8 onboard I/O card slots
- Install any combination of Q-SYS I/O Cards (Discontinued) for maximum flexibility
- Audio, video and control processing on a dedicated Linux™ realtime OS
- Software configurable as either a Core 510i processor, or an I/O-510i expander
- Built using standard computer industry hardware and IT industry networking protocols
- Control and integrate external devices using TCP/IP, RS232 and GPIO
- Design with powerful and intuitive Q-SYS Designer Software application
- Seamlessly integrates with Q-SYS AV-to-USB bridging peripherals
- Provides simple integration with QSC amplifiers and loudspeakers
- Multiple levels of system redundancy
The Core 510i is configurable in Core Mode or Peripheral Mode. By default, the Core 510i ships from the factory in Core Mode. It's easy to switch modes.
- Open Core Manager for the Core 510i.
- From the Utilities menu, change the Mode property to 'Peripheral'.
- Click Switch.
Once the device reboots, you can then configure it using Configurator > Peripheral Manager. In your design, add the I/O-510i to your design from the Inventory > Audio - Q-LAN menu. Once you save and run your design to the Core, the I/O-510i will then be functional as a peripheral after its firmware updates.
- From Configurator (Tools > Show Configurator), locate the I/O-510i from the I/O Devices category.
- Click the device to open Peripheral Manager.
- From the Utilities tab, change the Mode property to 'Core'.
- Click Switch.
Once the device reboots, you can then configure it using Core Manager. In your design, be sure to change Core Properties > Model to 'Core 510i'. Once you save and run your design to the Core, the Core 510i will then be functional as a Q-SYS Core processor after its firmware updates.
The following Q-SYS Designer components are available for the Core 510i, depending on its Properties:
Standard Components
- Status (Core)
- GPIO (Core 510i, 1100, 3100, I/O Frame)
- Loudspeaker Monitor
- Serial Port (Core, I/O Frame, I/O-22)
I/O Card Components
For a description of individual I/O card hardware, see I/O Cards (Discontinued).
Front Panel
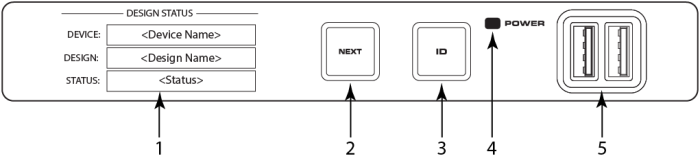
- OLED Display – Displays information about the Core's settings and status.
- NEXT button – Cycles through the OLED information pages
- ID button – Locates the Core in Q-SYS Designer GUI and Configurator
- POWER LED – Illuminates blue when the Core is on
- USB Ports – USB Type A Host connectors (2)
Rear Panel

- Eight Audio I/O Card Bays – Accept Q-SYS Type 2 Audio I/O Cards (supports up to 128x128 local audio channels)
- GPIO A and GPIO B – Female DA-15 connectors for Q-SYS control I/O
- RS232 – Male DE-9 serial communications interface
- HDMI – Video Output
- AC Mains – IEC 60320 C14 receptacle
- AUX LAN – RJ45: Data, VoIP, WAN streaming, management Auxiliary Ports – USB Type A Host Ports
- LAN A – RJ45: Q-LAN, AES67, Audio, VoIP, management Auxiliary Ports – USB Type A Host Ports
- LAN B – RJ45: Q-LAN, AES67, Audio, VoIP, management
Design Status
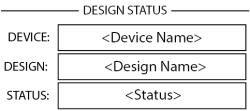
- Device – The name of the Core as defined in Q-SYS Designer.
- Design – The name of the currently running design.
- Status – Indicates health of Core in design:
- OK – Audio, Video and Control (AVC) engine is good.
- Compromised – AVC engine is good, but a redundancy mechanism is active (one LAN down but the other is still up) or a non-fatal hardware problem exists (fans too slow, temperature higher than expected, etc.)
- Fault – AVC engine is stopped, or hardware is malfunctioning or mis-configured
- Missing – A piece of hardware, defined in the design, has not been discovered. AVC engine is not communicating with that piece of hardware.
- Initializing – Starting the firmware, configuration update, or design update.
- Not Present – A virtual component in the design, that is designated as Dynamically Paired, and Not Required, has no hardware assigned to it.
System Status

- Firmware – A three-section number identifying the major release, minor release, and maintenance release. For example, 6.0.0.
- Temp – The current chassis temperature of the Core.
- Fan Speed – This number varies with the temperature.
LAN A

- Static or Auto – Displays next to LAN A, indicates if the Core's IP Address is Static or Automatic.
- IP Address – The IP Address assigned to the Core's LAN A. LAN A is the primary Q-LAN connection to the Core, and is required.
- Net Mask – The Net Mask assigned to the Core.
- Gateway – The Gateway assigned to the Core.
Note: You can edit this information in Core Manager.
LAN B
LAN B is used for redundancy or segregation of various data types on to different networks but is not required for device operation. The information is displayed in the same format as LAN A.
LAN AUX
LAN AUX is used for remote monitoring, WAN and VOIP connectivity, and is not required. The information is displayed in the same format as LAN A.
Slots A - H
There is a total of 8 slots that can accommodate any combination of Q-SYS I/O Cards that are Type 2 format. The status for these cards are shown on the front panel by pressing the NEXT button.

The Mic/Line In H.P. card status screen shows the Mute state, Signal presence, Clip indication and +48V state of each of the 4 input channels.
- Mute – Displays a "muted loudspeaker" when the channel is muted.
- Signal – Displays a solid circle when there is a signal present on the associated channel.
- Clip – Displays a solid circle under the channel having an output signal over driving the associated channel output.
- +48V - Displays a sold circle when phantom power is active on the associated channel.

The Mic/Line In Standard card status screen shows the Mute state, Signal presence, Clip indication and +48V state of each of the 4 input channels.
- Mute – Displays a "muted loudspeaker" when the channel is muted.
- Signal – Displays a solid circle when there is a signal present on the associated channel.
- Clip – Displays a solid circle under the channel having an output signal over driving the associated channel output.
- +48V - Displays a solid circle when phantom power is active on the associated channel.
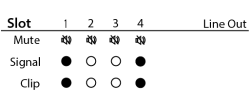
The Line Out card status screen shows the Mute state, Signal presence, and Clip status of each of the 4 output channels.
- Mute – Displays a "muted loudspeaker" when the channel is muted.
- Signal – Displays a solid circle when there is a signal present on the associated channel.
- Clip – Displays a solid circle under the channel having an output signal over driving the associated channel output.
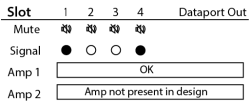
The Dataport Out card status screen shows the Mute state, Signal presence, and connected amplifier status for both ports.
- Mute – Displays a "muted loudspeaker" when the channel is muted.
- Signal – Displays a solid circle when there is a signal present on the associated channel.
- Amp 1 – Displays the status of the connected amplifier.
- Amp 2 - Displays the status of the connected amplifier.
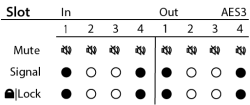
The AES3 card status screen shows the Mute state, Signal presence, and Lock state for 4 input and 4 output channels.
- Mute – Displays a "muted loudspeaker" when the channel is muted.
- Signal – Displays a solid circle when there is a signal present on the associated channel.
- Lock – Displays a solid circle when the AES3 clock is in sync and locked.
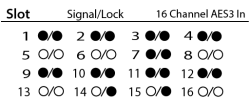
The AES3 16 channel card status screen shows the Signal presence, and Lock state for all 16 input channels.
- Signal – Displays a solid circle when there is a signal present on the associated channel.
- Lock – Displays a solid circle when the AES3 clock is in sync and locked for the associated channel.
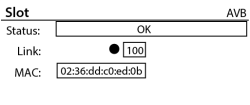
The AVB card status screen shows the Status of the card, Link state and speed of the network connection, and the MAC address of the card itself.
- Status – Displays the status of the AVB card.
- Link – Displays a solid circle when there is a valid connection with an AVB network or device and indicates the network connection speed in Mbps.
- MAC – Displays the MAC (Media Access Control) address of the AVB card.

The CobraNet card status screen shows the Activity state, Fault state, In Use state and Conductor state of the Primary and Secondary network ports.
- Activity – Displays a solid circle when the Primary or Secondary port is active.
- Fault – Displays a solid circle under the channel having a communication fault while sending or receiving a bundle.
- In Use – Displays a solid circle when there is an active connection to a CobraNet network or device on the associated LAN port (primary or secondary.) The image shows that the secondary port is active.
- Conductor - Displays a solid circle when the Primary or Secondary port is the Conductor.
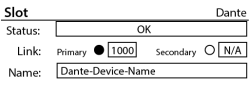
The Dante card status screen shows the Status of the card, Link state and connection speed of the Primary and Secondary network ports, and the Name of the device as seen by other Dante devices on the network.
- Status – Displays the status of the Dante card.
- Link – Displays a solid circle when there is a valid connection with a Dante network or device. The image shows that the Primary port has established a link at 1000 Mbps.
- Name – Displays the name of the Dante device that will be seen by other connected Dante devices.
GPIO Pin Assignments
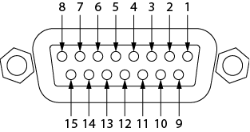
|
DB15 Pin |
Signal Name |
Signal Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
RNO |
Relay Contact |
Relay - normally open |
|
2 |
RNC |
Relay Contact |
Relay - normally closed |
|
3 |
GPIO 1 |
GPIO Current |
GPIO pin |
|
4 |
GPIO 3 |
GPIO Current |
GPIO pin |
|
5 |
POWER |
Power |
+ 12V DC |
|
6 |
GPIO 5 |
High Current |
GPIO pin -high current capable |
|
7 |
GPIO 7 |
High Current |
GPIO pin -high current capable |
|
8 |
GND |
Ground |
Ground |
|
9 |
RC |
Relay Contact |
Relay - common |
|
10 |
GND |
Ground |
Ground |
|
11 |
GPIO 2 |
GPIO Current |
GPIO pin |
|
12 |
GPIO 4 |
GPIO Current |
GPIO pin |
|
13 |
POWER |
Power |
+ 12V DC |
|
14 |
GPIO 6 |
High Current |
GPIO pin -high current capable |
|
15 |
GPIO 8 |
High Current |
GPIO pin -high current capable |
GPIO Specifications
Input Type |
Range |
|
Maximum Input Range |
0 V to 32 V |
|
Analog Input Range |
O V to 24 V |
|
Digital Input: Low |
0 V to 0.8 V |
|
Digital Input: High |
O V to 2.0 V |
Output Type |
|
|
Digital Output: Low |
0 V to 0.4 V |
|
Digital Output: High |
2.4 V to 3.3 V |
|
Digital Output Impedance |
1K Ohm |
|
High Current Output: Low |
0 V to 0.4 V |
|
High Current Output: High |
11 V to 13 V |
|
High Current Output: Sink or Source |
280 mA |
|
Relay Input and Output |
0 V to 30 V; 1 Amp |
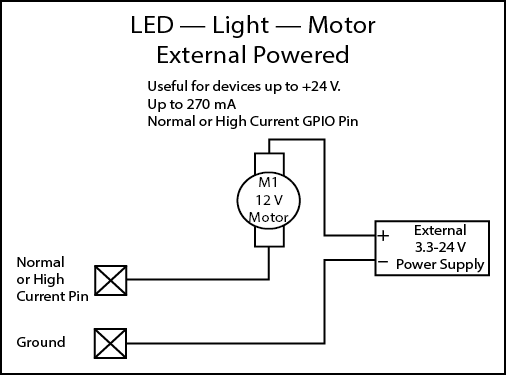
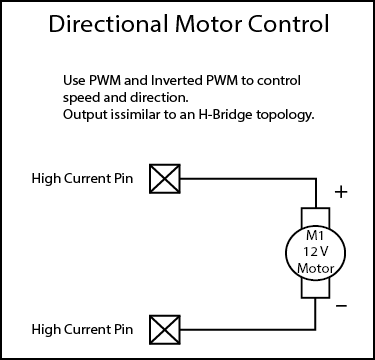
Note: The maximum current sourced by one GPIO connector (including both High Current and Power Pins) is 400mA.
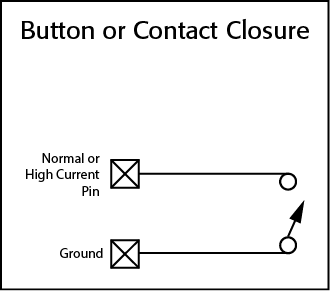
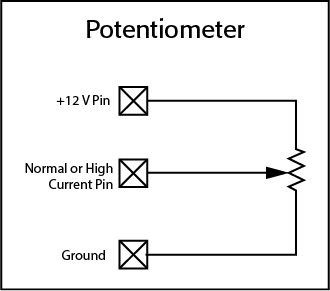
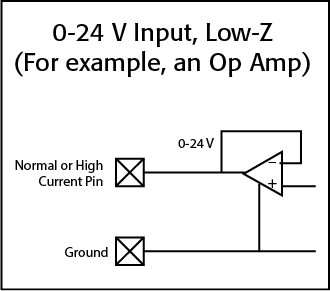
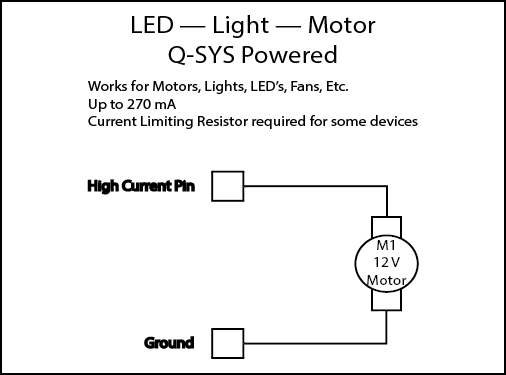
GPIO Examples
Refer to the Specifications Sheet on the Core 510i product page at qsys.com.