System Link
Use the System Link Transmitter and System Link Receiver components to move AV streams and multicast audio from one Q-SYS System to another. For example, you could transmit audio and video from a primary location (such as a main auditorium) simultaneously to a secondary location (such as an overflow room).
These Q-SYS Core processors support the System Link components:
The System Link components support:
- AV streams: Q-SYS Shift™ generated audio + video streams from the NV-32-H Network Video Endpoint.
- Multicast audio: Audio channels from inside Q-SYS, but transmitted in multicast. (Compare to Q-LAN TX and RX, which are unicast only.)
Note: The System Link components do not support control signals, paging signals, camera streams, or unicast audio streams.
- Because the System Link components create multicast streams for both AV streams and audio channels, you must configure the network for multicast traffic. Refer to Multicast Traffic in the Q-SYS Networking requirements section.
- Both Systems must be able to discover each other on the network.
- PTP settings for each System must match. Configure PTP settings in Q-SYS Designer from File > Design Properties.
Input Pins
AV Input 
The AV Input pins receive the combined HDMI video and audio signals for transmission to a System Link Receiver component in another Q-SYS System. Wire each AV Input pin to an upstream AV Output pin on an HDMI I/O (NV-32-H) Encoder component. The number of AV Input pins is configurable in the component Properties.
Input 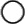
The audio Input pins receive multicast audio from upstream sources for transmission to a System Link Receiver component in another Q-SYS System. The number of Input pins is configurable in the component Properties.
Output Pins
This component has no output pins.
Input Pins
This component has no input pins.
Output Pins
AV Output 
The AV Output pins represent the combined HDMI video and audio signals received from the System Link Transmitter component in another Q-SYS System. Wire each AV Output pin to an AV Input pin on an HDMI I/O (NV-32-H) Decoder component. The number of AV Output pins is configurable in the component Properties.
Output 
The audio Output pins represent multicast audio received from the System Link Transmitter component in another Q-SYS System. Wire each audio Output pin to a downstream audio component. The number of Output pins is configurable in the component Properties.
In this example, there are two rooms: A main auditorium and an overflow room. Each room has its own Q-SYS Core processor running an AV design (a Q-SYS System).
The Main Auditorium System contains three HDMI sources – a camera, PC, and laptop – that an NV-32-H Encoder multicasts to both the in-room NV-32-H Decoder as well as a System Link Transmitter. The Transmitter also receives four channels of mic and program audio from the auditorium. The Transmitter sends the AV and audio signals from the auditorium to a System Link Receiver in the Overflow Room System, where the AV signals are routed to the room's display and the auditorium's audio signals are mixed with the overflow room's audio and routed to the room's speakers.
Main Auditorium System
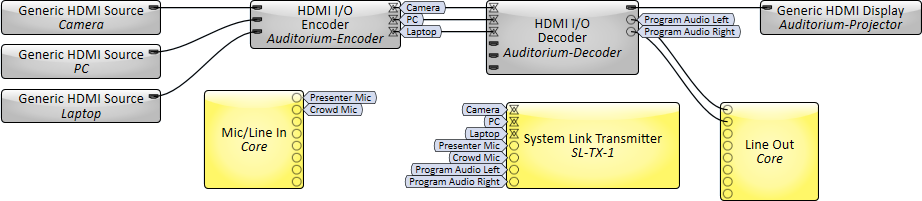
Overflow Room System
Name
The Name may contain ASCII letters 'a' through 'z' (case-insensitive), the digits '0' through '9', and the hyphen. Names cannot begin or end with a hyphen. No other symbols, punctuation characters, or blank spaces are permitted.
Location
User-defined name that groups the component with other components in the same physical location, or in the same organizational scheme.
Audio Channel Count
The number of multicast audio input pins, from 0 to 8 (default is 2).
AV Stream Count
The number of AV input pins, from 0 to 32 (default is 1).
Dynamic Stream Name
When set to 'Yes' (default), the Stream Name control name can be modified at run-time. In the Receiver property, this determines the Transmitter from which to receive AV and multicast audio signals. When set to 'No', the Stream Name always matches the Name of the component.
Status
The System Link Transmitter's status is conveyed with both an LED and status box:
- OK: The device is functioning normally. The number of connected clients is indicated.
- Compromised: The device is functioning, but a non-fatal problem exists. Refer to the Status box for details.
- Fault: The device is malfunctioning or is not properly configured. Refer to the Status box for details.
AV Streams
Stream Name
The Stream Name identifies the connection between a Transmitter and a Receiver. The default Stream Name is the name of the component as specified in Properties. Connected pairs must have the same Stream Name. If you leave the Stream Name at its default setting, at least one component (Transmitter or Receiver) must have its Dynamic Stream Name property set to 'Yes' with the stream renamed to match the other.
Streaming (LED)
Indicates if the source is streaming. Each AV Input has its own LED.
Audio
Q-LAN > Peak Output Level (dBFS)
Meters for each channel indicating the peak output level, from -120 to 20dB.
Digital > Clip
Indicates that the channel output is clipping.
Digital > Clip Hold
When toggled, the Clip LED remains on until reset.
Digital > Invert
Click to invert the polarity of the digital output of the signal.
Digital > Mute
Click to mute the output signal.
Digital > Gain
Adjust the gain of the output signal, from -100 to 20dB.
Audio Details > RTP Address
Combo box indicates the current multicast address being used for audio transmission, and also allows you to change the address.
Note: The RTP address is automatically selected, and should not be changed unless a network administrator requires it.
Audio Details
Text indicates the details of the Transmitter stream. The information in this field is updated regularly and is cumulative. Click Reset Details to set all counts back to zero.
Status
The System Link Receiver's status is conveyed with both an LED and status box:
- OK: The device is functioning normally. The Receiver indicates that it's connected to a Transmitter: "Server Connected".
- Compromised: The device is functioning, but a non-fatal problem exists. Refer to the Status box for details.
- Fault: The device is malfunctioning or is not properly configured. Refer to the Status box for details. For example, a Receiver will be in a fault condition if the design's PTP Domain does not match the PTP Domain of the Transmitter's Core, or if the Receiver is not connected to the Transmitter - "Server not connected". Refer to the Network Requirements section.
AV Streams
Stream Name
The Stream Name identifies the connection between a Transmitter and a Receiver. The default Stream Name is the name of the component as specified in Properties. Connected pairs must have the same Stream Name. If you leave the Stream Name at its default setting, at least one component (Transmitter or Receiver) must have its Dynamic Stream Name property set to 'Yes' with the stream renamed to match the other.
IP Streaming (LED)
Indicates if the source is streaming. Each AV Output has its own LED.
SRTP Address
Displays the address that the source is using to send the streaming data over the network.
Audio
Q-LAN: Peak Input Level (dBFS)
Meters for each channel indicating the peak input level, from -120 to 20dB.
Digital > Invert
Click to invert the polarity of the digital output of the signal.
Digital > Mute
Click to mute the output signal.
Digital > Gain
Adjust the gain of the output signal, from -100 to 20dB.
Audio Details > RTP Address
Indicates the current multicast address being used for audio transmission.
Audio Details
Text indicates the details of the Transmitter stream. The information in this field is updated regularly and is cumulative. Click Reset Details to set all counts back to zero.
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Audio Details |
||||
|
Details |
(text) |
Output |
||
|
Reset |
(trigger) |
Input / Output |
||
|
RTP Address |
(text) |
Input / Output |
||
|
AV Stream n |
||||
|
Streaming |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Output |
|
Channel n |
||||
|
Clip |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Output |
|
Clip Hold |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Gain |
-100 to 20 |
-100dB to 20dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Invert |
0 1 |
normal inverted |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Level |
-120 to 20 |
-120dB to 20dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Output |
|
Mute |
0 1 |
unmuted muted |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Dynamic Stream Name |
(text) |
Input / Output |
||
|
Status |
(text) |
Output |
||
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Audio Details |
||||
|
Details |
(text) |
Output |
||
|
Reset |
(trigger) |
Input / Output |
||
|
RTP Address |
(text) |
Output |
||
|
AV Stream n |
||||
|
SRTP Address |
(text) |
Output |
||
|
Streaming |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Output |
|
Channel n |
||||
|
Gain |
-100 to 20 |
-100dB to 20dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Invert |
0 1 |
normal inverted |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Level |
-120 to 20 |
-120dB to 20dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Output |
|
Mute |
0 1 |
unmuted muted |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Dynamic Stream Name |
(text) |
Input / Output |
||
|
Status |
(text) |
Output |
||
A System Link Transmitter or Receiver is capable of handling a maximum of eight channels of multicast audio and 32 AV streams.
Refer to Network Requirements.
Yes, AV Streams (Q-SYS Shift) can be sent across System Link.
- Unlike the System Link components, Q-LAN TX/RX is not capable of sending AV streams.
- Q-LAN TX components create individual unicast streams for each downstream RX unit. System Link TX creates a single multicast stream for all downstream RX units.
