Q-LAN Receiver
The Q-LAN Receiver, in combination with the Q-LAN Transmitter, provides audio streaming between two Q-SYS Core processors on the same LAN.
- Each Core must be set to the same PTPv2 Domain in the Design Properties. If the domains are not set to Custom, and you attempt to run the design, an error message is displayed indicating that the clock is not set correctly.
- The Q-LAN TX and RX components support unicast streams only: one transmitter can stream to one receiver. For a multicast option, see System Link.
Note: The number of signal pins is variable and set in the component's Channel CountProperty.
Input Pins
This component does not have any input pins.
Output Pins
Output 1 - n
Audio signal pins are represented by a (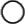 ) circle, and traditional wiring is represented by a thin black line.
) circle, and traditional wiring is represented by a thin black line.
By default, the Q-LAN Receiver component is set to 8 outputs. You can choose between 1 and 16.
Tip: For additional properties not listed, refer to the Properties Panel help topic for more information.
Q-LAN Receiver Properties
Dynamic Stream Name
When enabled, the Stream Name field in the Control Panel can be edited.
Channel Count
Number of channels for the Receiver. This count must match that of the Transmitter.
Stream Tab
Q-LAN
Peak Input Level (dBFS)
Meters for each channel indicating the peak input level.
Digital
Invert
Toggle button to invert the digital output of the Q-LAN Receiver.
Mute
Mutes the output signal.
Gain (dB)
Controls the Gain of the digital output signal.
Status
OK LED
LED indicating the status of the Receiver network link for both LAN A and LAN B (If network redundant).
Status
Component status is conveyed with the Status LED and Status box, which uses both color and text to indicate the current condition:
- OK: The device is functioning normally.
- Initializing: The device is in the process of a firmware, patch, or configuration update, or the design is starting.
- Compromised: The device is functioning, but a non-fatal problem exists. Refer to the Status box for details.
- Missing: The device cannot be discovered.
- Fault: The device is malfunctioning or is not properly configured. Refer to the Status box for details.
- Unknown: This status appears during a Core reboot (for example, during a firmware update), or when a design is being uploaded to the Core and before it has started running.
- Not Present: If applicable to the device, this status appears when the device is not connected to the network and its Is Required component property is set to 'No'. This status also appears if the device component's Dynamically Paired property is set to 'Yes', pairing has not been assigned in Core Manager, and the device component's Is Required property is set to 'Yes'. See Dynamic Pairing.
Connection
Stream Name
The Stream Name identifies the connection between a Q‑LAN Transmitter, and a Q‑LAN Receiver. They must have the same Stream Name.
You can leave the Q‑LAN Receiver or Transmitter at the default setting, but at least one must be set to Dynamic Stream Name = yes in the Properties then rename the stream to match the other.
Primary OK
This LED indicates if the Primary Stream is OK or not.
Backup OK
If your Core is redundant, you can choose to have your Q‑LAN receiver / transmitter redundant.
This LED indicates if the Backup Stream is OK or not.
Network Rx Buffer
Adds extra buffer time to the default maximum of 1 ms.
Additional Network Receive Buffer time is useful in (rare) cases where the network latency through the network exceeds the default maximum. Additional network latency my be introduced by sub-optimal QoS functionality, some layer-3 routing implementations, long distances or large networks.
Details Tab
LAN A / LAN B
Details
Text indicating the Details of the receiver stream. The information in this field is updated regularly and is cumulative. The information is displayed as running totals. Below is an example of some of the possible data.
- connected
- dscp
- accept_count
Reset Details
This button resets the networking details to zero, at which point the details start accumulating information again.
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Channel 1 – n |
||||
|
Gain |
-100 to 20 |
-100 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Invert |
0 1 |
normal invert |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Level (Peak Input) |
-120 to 20 |
-120 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Output |
|
Mute |
0 1 |
unmute mute |
0 1 |
Output |
Details |
||||
|
LAN A / B Details |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
LAN A / B Reset button |
Trigger |
Output |
||
Status |
||||
|
OK LED |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Output |
|
Status |
0 1 2 3 4 |
OK (green) Compromised (orange) Fault (red) Unknown (red) Updating (blue) |
0 0.250 0.500 0.750 1.00 |
Output |
Connection |
||||
| Backup / Primary OK LED |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Output |
|
Network RX Buffer |
Text Field: Default Extra 1 ms Extra 2 ms Extra 5 ms |
Input / Output |
||
|
Stream Name |
Text |
Input / Output |
||
Control Link: Control Signals.
Core-to-Core Paging: Paging Communication.
Q-LAN Transmitter: Unicast Audio Streams.
System Link: AV Streams & Multicast Audio Streams.
Q-LAN Bandwidth Compile Error
You cannot achieve both max stream and channels at the same time. The max stream count needs to be 256 to allow 256 single-channel streams. Configurations of 256x2 thru 256x16 all exceed line bandwidth.
