Using Controls
Controls are found on the control panel for each component. Controls are considered to be anything, other than text labels, that you find on a control panel; this includes graphs, meters, knobs, and so on. To display the control panel, add the component to the Schematic, then double-click the component; the control panel displays.
Controls behave differently depending on the mode of Q-SYS Designer.
- Run mode - all controls are active. Adjustable controls can be changed and will have an effect on the audio. Graphs, meters, and so on are active and display current information. Some graphs have "handles" you can move using your mouse, their movement is connected to a control on the same control panel.
- Emulate mode - all adjustable controls are active, control logic can be tested, but there is no audio passing therefore, no effect on audio. Graphs, meters are not active.
- Design mode - none of the controls are active, you cannot adjust them, if any information displayed on a control, it is from an earlier Emulate, or Run mode.
You can view a list of all controls for a selected component in your design. For named components, you can then use these control names for external control and control scripting. (For information on renaming components, see Labeling Schematic Elements.)
- In your schematic, select a component.
- From the main menu, select Tools > View Component Controls Info.
- A list of all controls for the component is shown in a window. Note that you can copy one or more control names from this window.
- You can then enable code access using the Code Name and Script Access Properties for any of the Component Controls.
- For a list of all available properties and metadata, see Controls IO.
There are a number of ways controls can be adjusted, including, External Control, Control Scripting, and manually. This topic address the manual method.
Basic
- Knobs and faders - click-and-hold the left mouse button on the control. Move the mouse up, down, left or right. The control adjusts with your mouse movement.
- Buttons - click the button. The button changes state according to the type of button, toggle, momentary, trigger, and so on.
- Drop-down lists - click the drop-down list, scroll or move the mouse to the entry you want, then click that entry.
- Meters - A read-only control that displays the level, gain, or reduction of a signal.
- Text box - A read-only control displaying a value or condition.
- Text Edit box - A text entry field. Enter the required text and click away from the box.
Keyboard Entry
Entering the value for a control offers a more precise way of adjusting the control. For numeric controls, the precision depends on the unit of measure, or value range, you may or may not be able to use decimals. To use the keyboard to adjust a control:
- Click the control, or hover the mouse cursor over the control.
- Enter the value. The value can be a number, item from the drop-down list, state of a button (mute, unmuted)
- Press the Enter key, or click away from the control. The value is changed.
Notes:
- Keyboard entry is limited by the range of the control. If you enter a value larger than the range, the control is set to the maximum value allowed, if the value entered is smaller than the lowest range value, the control is set to the lowest value.
- Precision of the display value (below a control) is typically limited by the number of characters allowed in that display area - usually a maximum of three digits (numeric) excluding the decimal point, minus (-) character, and the unit of measure (ms, dB, and so on). For example, you can enter 3.95, or 955m, and so on.
- Keyboard entries are rounded up at 5 in the display. For example, if you enter 0.000005 (seconds) or 0.0005m the control display is set to .001 ms.
Shortcuts
Time values, when entered via the keyboard, may be entered in milliseconds (ms) by typing an "m" after the value, or seconds by simply entering the value. If the number entered is greater than the range of the control in seconds, the entry is treated as milliseconds.
- For 2.00 ms, enter 2m or 0.002
- For 0.001 ms, enter .001m or 0.000001
Frequency values, when entered via the keyboard, may be entered in hertz by simply entering the value, or kilohertz by entering the value or 1/1000 of the value followed by the letter "k"
- For 120 Hz, enter 120
- For 17 kHz, enter either 17000 or 17k.
Adjust multiple controls of the same type at the same time. Select all the controls, enter a value or move the control.
You can use special commands, as detailed under the Push Action property, to set the value of numeric controls.
You can drag controls from a control panel into the Schematic by Adding Controls to a UCI Page. You can make them available for external control systems (see Named Controls), or place them in a Snapshot. The control , with the exception of a control in a Snapshot, is now a proxy for the actual control in the control panel. You can use it to make adjustments with out opening the control panel.
Control Properties
When you drag a control into the Schematic the following properties are available:
Button
A button for which you can set a push action.
Combo Box
Provides a drop-down list of the available parameters.
Fader
Provides an adjustable fader-type control. Can be vertical or horizontal.
Knob
Provides an adjustable knob-type control.
LED
Provides an LED. No adjustments available.
List Box
Provides a list of the available parameters. Scroll bars are available for long lists.
Media Display
Available for all text controls, converts a JSON-formatted URL string into media that displays in the text box. See Media Display.
Meter
Provides a meter. Can be horizontal or vertical.
Text Field
Provides a text box for text type readouts.
Presentation
Allows you to change the presentation style of the control.
You can change the presentation style in the Properties of the control, or you can copy the style from another control in the Schematic.
To copy the style from one control to another:
- Select the control you want to copy from.
- Hold the Ctrl button and drag the control over the control you want to copy to. (You can also drag the control over the other control, then press the Ctrl button.)
- Release the mouse button, a selection list displays.
- Select "Transfer Control Style". The "copy to" control now has the same Style as the "copy from" control.
Regardless of the style you select, the control reacts in the appropriate manner based on the control you select or the control from which it was copied. Not all selectable Styles may be appropriate for the original control. The options available are: Button, Combo Box, Fader, Knob, LED, List Box, Media Display, Meter, and Text Field.
Position
The coordinates reference a specific place in the schematic - for example,"100,100" (horizontal, vertical). 0,0 is the upper left corner of the schematic.
Size
The numeric size of the control. For example 70,32 (width, height).
Fill
Sets the Fill color of the button. The Fill color is the color of the button in its ON state.
Weight (Font)
Changes the weight of the Label. For the Text Field, this controls the text displayed or entered in the field in the Run or Emulate mode; it is not a Label.
Horizontal Alignment (Font)
Changes the alignment of the Label on a horizontal basis. For the Text Field, this controls the text displayed or entered in the field in the Run or Emulate mode; it is not a Label.
Vertical Alignment (Font)
Changes the alignment of the Label on a vertical basis. For the Text Field, this controls the text displayed or entered in the field in the Run or Emulate mode; it is not a Label.
Push Action
Sets the style of a Button. The following values are available:
- Momentary: When the button is clicked, it stays in its opposite state until released.
- Off: Sets the value of the button to "off" (or 0, or false). Clicking the button again does not turn it on. You can change the button to "on" (or 1, or true) by clicking the button in its Control Panel, or another copy of the button with any button Push Action except "Off".
- On: Sets the value of the button to "on" (or 1, or true). Clicking the button again does not turn it off. You can change the button to "off" (or 0, or false) by clicking the button in its Control Panel, or another copy of the button with any button Push Action except "On".
- String: When the button is clicked, it sends the string you entered to the control in the Control Panel. See Button String property.
- Toggle: Allows you to turn the button on or off.
Button String
Available when Push Action is set to 'String'. The string you enter is case sensitive and must be valid for the control in the Control Panel. For example a fader control has a range of -100 to 20, the string must be numeric and within that range, a toggle button must be true/false, On / Off, or 1/0.
In addition, the following special commands may be used in the String field:
- ++ moves the control plus 1 minor division
- -- moves the control minus 1 minor division
- += moves the control plus n major units where n = String value (ex.+=2)
- -= moves the control minus n major unit where n = String value (ex. -=2)
- *= moves the control n times the major unit where n = String value (ex. *=3) If the current value of the control is 0 (zero), the multiplication command will not move the control. If you enter 0 in the String field, the control moves to 0 (zero).
- max moves the control to its maximum value.
- min moves the control to its minimum value.
A Button with String Push Action in Q-SYS works differently compared to other buttons. Instead of a boolean 0 or 1 value, it interacts with the underlying control with a string value. Typically, Q-SYS buttons connect to controls with a numerical 0 or 1 value, but String Buttons connect with a controls with a user defined Button String.
For example, if you set the Button String to the value "5" and press it during operation, the string "5" is sent to the underlying control. This is the effectively the same as if you selected the control in Designer, typed On, and hit enter. Likewise, when the underlying control's value changes, the button compares its Button String to the controls string. The button is shown to be in the “on” state ( i.e., the :value(1) CSS selector).
In this example, discrete buttons are used to set a Gain component to a specific value.
- Copy the Gain control out of the Component
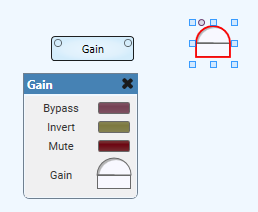
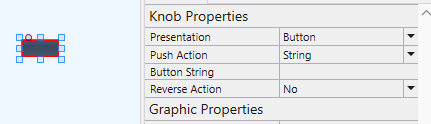
- Change
PresentationtoButton,Push ActiontoStringandButton Stringto3.00dB
- After emulating or deploying the Design, pressing the button will set the Gain to 3.00dB and be shown to be ‘on’
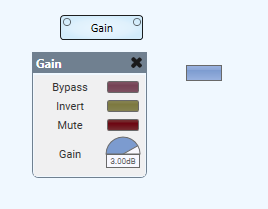
- Multiple copies of the button can be made, each with its own
Button String- i.e.,0dB,-6.00dB,12.0dB, etc.
Note: This string must match the value displayed in the control for the button to reliably show the ‘on’ state. For example, if the Button String is set to just 0 the Gain will go to 0dB when pressed but will not show ‘on’ since the strings do not exactly match.
Reverse Action
Changes the direction of the control.
For example, a gain control normally increases gain as the control moves clockwise; apply the Reverse Action, and the gain now increases by moving the control in a counterclockwise direction. This is useful, for example, if you want a gain control to appear to be increasing attenuation. Another example is if you want to change a mute button (on state is muted, off is passing audio) to an enable button (on state is passing audio, off state is muted).
Off Color
Sets the color of the button in its OFF state. When the link to the right of the Off Color patch is linked, the Off Color is linked to the Fill, or ON color, and changes when you change the Fill color. If you click the link, you can manually set the Off Color.
Corner Radius
Sets the radius of the button corners.
You can also adjust a control's corner radius using the corner radius handle.
Margin
Sets the size of the margin. The button stays the same size, but the visible part of the button is reduced equally around the button.
Padding
Controls the margin within the visible part of the button. If there is text and/or an icon, they are reduced in size to fit within the padded margins.
Icon
Select an icon from the list, or select Custom to select your own icon image (.png, .jpg, .jpeg, .gif, or .svg).
Note: You can also use Lua to Encode Icons to Buttons
Icon Color
Sets the color of the selected icon.
Icon Alignment
Determines the horizontal position of the icon when there is a text label on the button.
Button Style
Flat - The selected button is displayed without styling.
Gloss - The selected button is displayed with a shiny appearance.
Image - Select a custom image (.png, .jpg, .jpeg, .gif, or .svg) for the button. You can set separate images for On, Off, Pressed On, and Pressed Off states:
- On: Image that displays when the button is On.
- Off: Image that displays when the button is Off.
- Pressed On: Image that displays while actively pressing the button when toggling from Off to On.
- Pressed Off: Image that displays while actively pressing the button when toggling from On to Off.
Note: For information about using .svg files in a UCI, see User Control Interface (UCI) Design Overview.
Background Color
Sets the background color of a Meter control
Background
- Meter Background - Used primarily when you change a Meter type control into a Text Field. The value read by the Meter is displayed, in text, in the center of the graphical Meter, instead of in a Text field below the Meter.
- No Background - No background or outline; displays the text on the object or Schematic background. The Fill color controls the color of the text.
- Normal - Standard Text field. The background is controlled by the Fill color, the text is automatically set to a color contrasting with the Fill color.
Size (Font)
Changes the font size (in pixels) of the control's Label. This is the text you can type when the control is selected. For the Text Field, this controls the text displayed or entered in the field in the Run or Emulate mode; it is not a Label.
LED Style
Changes the style of the LED.
Fader Style
Set the style for the fader. With Custom, you can further adjust these properties:
- Cap Height: The height of the fader cap, from 0-400.
- Cap Radius: The corner radius of the fader cap, from 0-100.
- Cap Shadow: Select whether to apply a fader cap shadow.
- Slot Width: The width of the fader slot, from 0-100.
- Slot Radius: The corner radius of the fader slot, from 0-100.
Show Text Box
Displays the text read out of the control setting.
Meter Type
Sets the style of the Meter. All of the meter styles are RMS meters, the difference is the way they are displayed, and the legends used. The text box associated with the meter styles always reads RMS with the exception of the Meter component in Peak mode.
- Gain - The Gain meter uses the Digital Gain legend. The 0 (zero) point of the Gain meter is in the center of the meter, and equals -20 dB RMS. From the 0 point the meter reads up, in green, to indicate a positive gain and down, in red, to indicate attenuation or negative gain. See the Gated Ambient Compensator Gain meter for an example.
- Level - The Level meter uses the Digital dBFS legend. This meter is consistent with the RMS readings, i.e. 0 RMS input = 0 dBFS on the legend. See the Gated Ambient Compensator Detector meter for an example.
- Reduction - The Reduction meter uses the Digital Reduction legend. Reads down from 20 dB RMS (0 on the legend), in red, to indicate amount of attenuation applied to a signal. See the Gain Sharing Automatic Mixer for an example.
- RefMicLevelRatio - This meter indicates how much, in dB, the Far-End reference signal level exceeds the Near-End microphone signal level. Refer to Reference-to-Microphone Level Ratio (RMLR) for more information.
- Segmented - The segmented meter draws the meter in fixed discrete sections acting as individual LED lights that are either completely on or off based on the value of the meter. The Segment Count property determines the number of segments which are evenly distributed along the meter (must be a value between 3 and 100).
- Standard - The Standard meter uses the Digital dBFS legend. This meter is consistent with the RMS readings, i.e. 0 RMS input = 0 dBFS on the legend. The standard meter has a multi-color display from blue to yellow. Yellow indicates clipping. See the Meter for an example. The Meter component offers a selection between RMS and Peak. In the Peak mode the meter reads 3 dB higher than the RMS reading.
Meter Legend Style
Select a style of the legend, or scale, for a meter.
Note: For the Digital dBFS meter style, dBFS in Q-SYS is referenced to zero being the point at which the output of the D/A Converter will clip. Because of floating point capabilities, Q-SYS can read dBFS values above zero. The indication above zero dBFS lets you know that you need to bring the signal down before sending it to the D/A Converter.
Refer to Aligning Schematic Elements for details.
Each control you place in the Schematic has a "behind-the-scenes" Control ID that ties it to the specific component it came from. The Control ID allows you to use a copy of the control in the Schematic, in Snapshots, UCIs, and External Control systems. The Control ID cannot be changed, but it can be copied from one control to another.
In addition, you can copy the Style of one control to another.
- Select the control you want to copy from.
- Hold the Ctrl button and drag the control over the control you want to copy to. (You can also drag the control first, then press the Ctrl button.)
- Release the mouse button, a selection list displays.
- Do one of the following
- Select "Remap Control". The "copy to" control now has the same Control ID as the "copy from" control, regardless of the control's style.
- Select "Transfer Control Style". The "copy to" control now has the same Style as the "copy from" control.
Tip: If you need to remap many UCI controls between components or within the same component, use the Remap UCI Controls [BETA] tool.
Polygon Control
You can make a shape using the Polygon tool then transfer the settings from a control to the polygon shape. The procedure is the same as above, with the exception that it copies both the Control ID and the Control Style in one operation.
- The polygon shape is always a button type control.
- You can copy or duplicate a polygon shape along with the assigned control's properties, then assign a different button style if you want to.
- You can not copy properties from a polygon shape control to another control, including another polygon shape.
You can copy all of a component's control settings to the same type of component. For example, if you have configured a Delay Matrix Mixer, you can copy all of its control settings to a second Delay Matrix Mixer. With your design in Run or Emulate mode:
- In your schematic, select the component from which you want to copy all of the component's control settings.
- From the main menu, select Tools > Component Controls > Copy Component Controls.
- In your schematic, select another component of the same type as the first component.
- From the main menu, select Tools > Component Controls > Paste Component Controls.
You can give names or Labels to Button and Fader style controls by selecting the control and simply typing the name.
You can drag bitmap type pictures onto a button control. Select the file in Windows Explorer or copy from a graphics editor onto the button. Resizing the button resizes the picture proportionally. The button must be in the Schematic, not in a component's control panel.
