Serial Port (NV-32-H)
The NV-32-H includes an RS-232 connection for extension of Q-SYS Control to third-party devices, such as projectors, TVs, and A/V receivers. You can control and read from these devices using Lua script from a Q-SYS scripting component.
Tip: To learn about scripting in Q-SYS, see Control Scripting.
The Serial Port component represents the RS-232 serial connection pins on the rear of the NV-32-H.
Note: On the NV-32-H, the RS-232 and GPIO IN pins share a 5-pin Euro connector. You can use both connection types simultaneously.
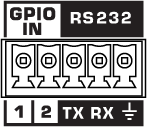
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
|
TX |
Transmit pin. Connect this pin to the RX (receive) pin on the other device. |
|
RX |
Receive pin. Connect this pin to the TX (transmit) pin on the other device. |
|
Ground |
Earth ground reference for GPIO input and RS-232 connections. |
The Serial Port component represents the RS 232 connector on the rear of the NV-32-H.
Input Pins
This component has no input pins.
Output Pins
Serial Port 
Connect this pin to the Serial Input pin of a Q-SYS scripting component, such as Block Controller, Text Controller, or Control Script. You must configure these components for serial communication.
Tip: For additional properties not listed, refer to the Properties Panel help topic for more information.
The Serial Port has no unique Properties. See the HDMI I/O (NV-32-H) for specific properties.
TX Bytes
Displays a running total of the number of transmitted bytes of data.
RX Bytes
Displays a running total of the number of received bytes of data.
Reset
Click to reset the TX Bytes and RX Bytes counters to zero.
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Receive Bytes |
(text) |
Output |
||
|
Reset |
(trigger) |
Input/Output |
||
|
Transmit Bytes |
(text) |
Output |
||
Check the pinout of any equipment, including the cable, to be connected to a Q-SYS serial port for input or output. In many cases, you can solve serial communication problems by inserting a null modem adapter or cable to swap the TX and RX pin positions. The TX pin on one end must be connected to an RX pin on the other end (and vice versa) for data to flow properly.
