Status/Control (Softphone)
The Q-SYS Softphone gives you the ability to connect to a Voice-over-IP telephone system (IP-PBX) or SIP-based devices without the need for telephony hardware. You can also use the Softphone component in unregistered mode, which allows for making ad-hoc IP-to-IP calls and connecting to other non-registered SIP-compatible equipment.
Compatibility
- Q-SYS Softphone is a VoIP/SIP system that directly supports digital phone systems and direct VoIP calls. To connect to an analog system, you can use an FXO Gateway that has analog POTS inputs, a network output, and can be configured to route incoming analog to the Q-SYS Softphone.
- Q-SYS supports most ITU standard codecs. Refer to the Q-SYS Core Manager Telephony > Softphones topic.
Note: Microsoft Teams and Webex do not natively support third-party SIP devices. For Microsoft Teams, a Session Border Controller (SBC) is required – see the Plan Direct Routing page from Microsoft for more information. Alternatively, we recommend using Q-SYS USB Bridging with these services instead. See the USB Audio Bridge and USB Video Bridge topics for more information.
Configuration
- Use the Q-SYS Core Manager > Telephony > Softphones page to configure registration with IP-PBX systems such as Cisco CUCM, FreeSwitch, etc.
- Refer to the SIP Conferencing Integration topic for guidance on configuration.
Maximum Softphones per Design
Note: Q-SYS Scaling Licenses expand the capabilities of some Q-SYS Core processor models. Refer to the Licensing topic for more information.
| Core Model | Max Softphones |
|---|---|
|
NV-32-H (Core Mode) |
1 |
|
Core Nano |
2 |
|
Core 8 Flex |
2 |
|
Core 110f |
4 |
|
Core 110c |
1 |
|
Core 510i |
64 |
|
Core 510c |
4 |
|
Core 5200 |
64 |
| Discontinued | |
|
Core 250i |
64 |
|
Core 500i |
64 |
|
Core 1100 |
64 |
|
Core 3100 |
64 |
A single Softphone consists of the following:
- Status/Control component - This component is the controlling component. It has a numeric keypad, displays the incoming call information, has various controls including Do-not-disturb, Auto Answer, Dial, Hang-up, and displays status information.
- VOIP In component - This component provides and controls the audio input signal from the incoming call.
- VOIP Out component - This component provides the audio output connection and controls the outgoing audio signal level.
- Softphone configuration (Q-SYS Core Manager) - This is where you enter the Softphone parameters. These settings are available once a Softphone is in the Q-SYS design.
Note: Refer to the Telephony > Softphones topic in Core Manager Help to learn how to configure Softphone on the Q-SYS Core processor and to see a list of compatible VoIP providers.
Below is a very simple illustration of how you can set up the Q-SYS Softphone in a design; there are a number of other ways.
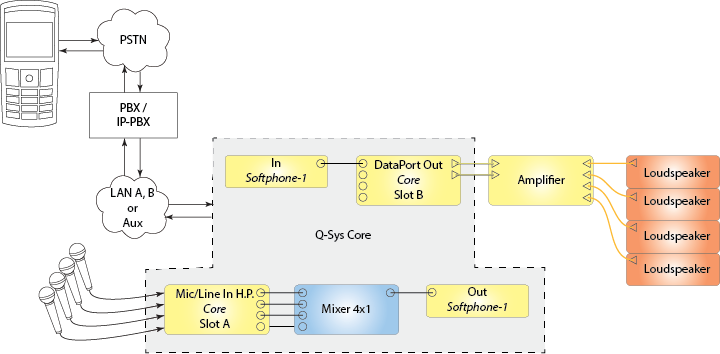
To enhance your Q-SYS Softphone implementation, you can add various components from the Schematic Library. Below is another conference-room implementation, using the Q-SYS Acoustic Echo Canceler component. This particular design is available on the QSC Training website.
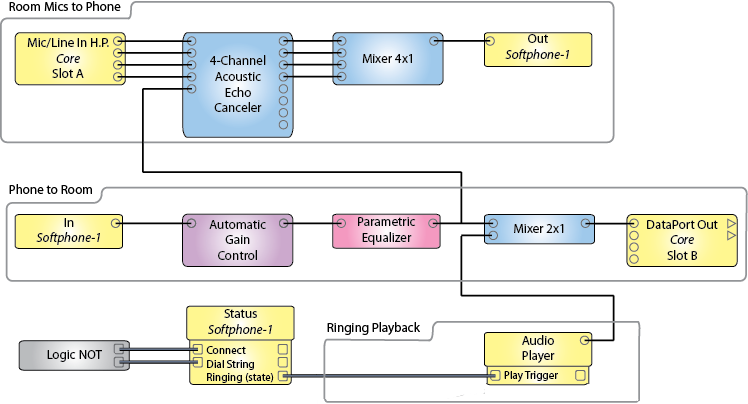
Tip: For additional properties not listed, refer to the Properties Panel help topic for more information.
Softphone Properties
Tone Output
When 'Yes' is selected, the Ring, Entry, Exit, and DTMF tones are fed to a separate output channel (Tone Output) on the VOIP In component. These tones can now be routed independent of the voice audio.
The Softphone can be exercised in the Emulation mode from Q-SYS Designer. This can be useful during the design phase to validate scripts or test certain logic without having to deploy the design on an actual core.
To use this feature, add a Softphone to the design and press F6 for Emulation. Open the Softphone dialer. You can place calls and also receive dummy calls.
- To place a call simply enter any number using the Pin-Pad or the Dial String field and click the Connect button. The call will be connected after 5 seconds.
- To receive a call click the "Simulate an Incoming Call" button that displays during Emulation. This button is present only during Emulation and when clicked, will place a call to the Softphone in which you clicked the button. All the relevant control pins will change states to reflect the call being placed or received.
Status/Control
Dial String
The number of the phone or device you are calling. This number is a text string entered by either the Keypad, keyboard, or using the Dial String Control Pin.
The "," symbol can be used to insert a 1 second Soft Pause in the dial string. (For example, dial string "729 832 9502 ,,,,, 19327#").
The ";" (semi-colon) symbol can be used to insert a Hard Pause into the dial string, to be used in conjunction with the 'Continue with…' feature described below (For example,dial string "729 832 9502 ; 19327#")
Note: Do not use a comma (,) directly next to a semi-colon (;) or two semi-colons directly next to each other.
Backspace Key
The Backspace key deletes the last character typed, and can continue deleting one character at a time.
Clear Key
The clear key (X) clears the entire Outgoing dial digits field.
Progress
Displays the CID number, the CID name (if available), and the call status of the incoming call. You can display these separately using the corresponding Control pins.
DND (Do Not Disturb) Button
Activating the DnD feature causes Q-SYS to ignore any incoming calls. If connected to an IP-PBX, that system handles the response given to the incoming caller. For example, busy signal, message, and so on.
Disconnect (Hang Up / Ignore) Button
Press this button to disconnect the call.
Connect (Dial / Answer) Button
Enter the Outgoing dial string then press this button to initiate the call. If there is an incoming call, press this button to answer the call.
Off Hook LED
This LED indicates that your call is active. It lights when the call is connected, and goes off when you press the Hang Up key or the line is disconnected.
Ringing LED
LED indicates that there is an incoming call, or there is an outgoing call waiting for the called party to answer.
Call Control Call Connect Time
Digital readout of the time the call has been connected.
Auto Answer Button
Enables and disables the Auto Answer feature. The button illuminates when the feature is active.
After # Rings
This parameter sets the number of rings before the Auto Answer feature answers the call.
Note: This control acts like a knob - click and drag to change, or key in the number of rings.
Keypad
This is a standard 12-key numeric keypad used to key in the Outgoing dial digits, or send DTMF while off hook. For example, you can enter additional numbers to navigate an answering system.
Recent Calls
List of recent calls, up to 100 maximum.
Clear
Clears recent call list.
Continue with ...
The 'Continue with …' control is used to submit pre-defined DTMF digits after an active call triggers a Hard Pause to assist with navigating IVR's and Conference Bridge dial in.
Simulate Incoming Call
Simulates an incoming call in Emulation mode to assist with development of UCI's and third-party integration when Q-SYS hardware or SIP Server is not available.
Status LED
Multi-color LED giving the status of the Softphone.
Status
This is a text field displaying details of the status of the Softphone. The color of this field matches the color of the LED.
Note: Ring Tone files – Q-SYS has a default set of ring tone .wav files in the Ring tones directory. You can access these files through the Q-SYS Core Manager > Files page.
Ring Tone
Enable
Enables the ring tone for incoming calls. This also configures the ring-back tone on outgoing calls. If the far end of the outgoing call provides a ring tone, that tone overrides this configuration.
Gain (dB)
Sets the level of the incoming call ring tone and, for outgoing calls, this sets the level of the ring-back tone.
Filename
Specifies the file to play for the incoming call's ring tone, and outgoing call's ring-back tone.
Entry Tone
Enable
Enables the entry tone for incoming calls. The entry tone indicates that the incoming call has been Auto-answered.
Gain (dB)
Sets the level of the incoming call ring tone and, for outgoing calls, this sets the level of the ring-back tone.
Filename
Specifies the file to play for the incoming call's entry tone.
Exit Tone
Enable
Enables the exit tone for incoming calls. The exit tone indicates that the incoming call has been disconnected (hung up).
Gain (dB)
Sets the level of the incoming call exit tone.
Filename
Specifies the file to play for the incoming call's exit tone.
Keypad Tone
Enable
Enables the playback of the DTMF digits sent from your Core as keypad tones.
Tone Gain
Sets the level of the keypad tones.
Filename
Specifies the file to play keypad tones.
Force Local Ringback
When enabled, the selected Ring Tone file will override the audible tone sent by the remote party. For example, when dialing an international number, the remote party may send an audible tone to be played back to the caller. This may not be desirable. To keep ring tones consistent (regardless of the outgoing number dialed), enable this option.
Note: This option has no effect if Ring Tone is disabled.
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Call Control Auto answer |
0 1 |
off on |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Call Control Auto answer Rings |
0 to 99 |
0 to 99 |
0.00 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Call Control Backspace |
Trigger |
Input / Output |
||
|
Call Control Clear |
Trigger |
Input / Output |
||
|
Call Control Connect |
Trigger |
Input / Output |
||
|
Call Control Dial String |
Text Edit Field |
Input / Output |
||
|
Call Control Disconnect |
Trigger |
Input / Output |
||
|
Call Control Do Not Disturb |
0 1 |
off on |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Call History Clear Call History |
Trigger |
Input / Output |
||
|
Call History Recent Calls |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
Call Status |
||||
|
Caller ID Date/Time |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
Caller ID Name |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
C Caller ID Number |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
Connect Time |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
Details |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
Off Hook |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Output |
|
Call Progress |
Text Field |
Output |
||
|
Ring (trigger) |
Trigger |
Output |
||
|
Ringing (state) |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Output |
|
State |
Text Field (inactive, active, outgoing, incoming) |
Output |
||
|
Tone Control (Configuration) |
||||
|
Configuration Entry Tone Enable |
1 0 |
enabled disabled |
1 0 |
Input / Output |
|
Configuration Entry Tone Filename |
Text |
Input / Output |
||
|
Configuration Entry Tone Gain |
-100 to 0 |
-100dB to 0dB |
0.00 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Configuration Exit Tone Enable |
1 0 |
enabled disabled |
1 0 |
Input / Output |
|
Configuration Exit Tone Filename |
Text |
Input / Output |
||
|
Configuration Exit Tone Gain |
-100 to 0 | -100dB to 0dB | 0.00 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Configuration Force local Ring Tone Enable |
1 0 |
enabled disabled |
1 0 |
Input / Output |
|
Configuration Local DTMF Echo Enable |
1 0 |
enabled disabled |
1 0 |
Input / Output |
|
Configuration Local DTMF Echo Gain |
-63 to 0 |
-163dB to 0dB |
0.00 to 1.00 |
|
|
Configuration Ringing Tone Enable |
1 0 |
enabled disabled |
1 0 |
Input / Output |
|
Configuration Ringing Tone Filename |
Text |
Input / Output |
||
|
Configuration Ringing Tone Gain |
-100 to 0 | -100dB to 0dB | 0.00 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
DTMF Rx |
Text Edit Field |
Output |
||
|
DTMF Tx |
Text Field |
Input / Output |
||
|
Pin Pad characters (One control pin for each character.) |
Trigger button input causes the triggered character to display in the Dial String field. |
Input / Output | ||
|
Simulate Incoming call from 1234 |
Trigger | Input / Output | ||
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Input Gain |
-100 to 20 |
-100 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Input Invert |
0 1 |
normal invert |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Input Mute |
0 1 |
unmute mute |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Input Peak Level |
-100 to 20 |
-100 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Pin Name |
Value |
String |
Position |
Pins Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Clip |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Clip Hold |
0 1 |
false true |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Output Gain |
-100 to 20 |
-100 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
|
Output Invert |
0 1 |
normal invert |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Output Mute |
0 1 |
unmute mute |
0 1 |
Input / Output |
|
Output Peak Level |
-100 to 20 |
-100 dB to 20 dB |
0.000 to 1.00 |
Input / Output |
| Acronym / Abbreviation | Explanation |
|---|---|
|
CID |
Caller ID |
|
DTMF |
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (for digital systems, this is numbers, not tones) |
|
FXO |
Foreign eXchange Office |
|
PBX |
Private Branch exchange |
|
POTS |
Plain Old Telephone Service (Analog) |
|
PSTN |
Public Switched Telephone Network |
|
SIP |
Session Initiation Protocol |
|
VoIP |
Voice over Internet Protocol |
|
VoIP‐PBX |
Digital version of the Private Branch exchange (Other abbreviations include IP-PBX, and IPBX.) |
